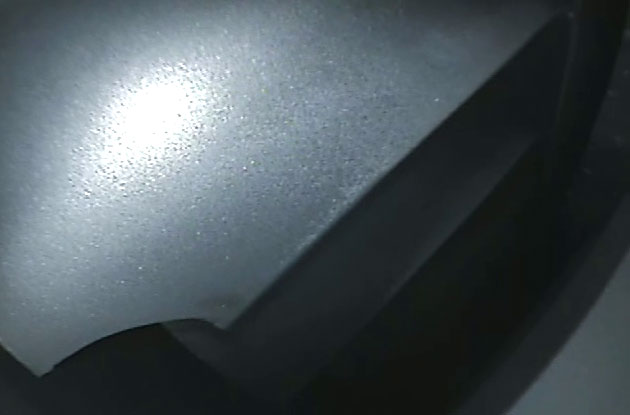
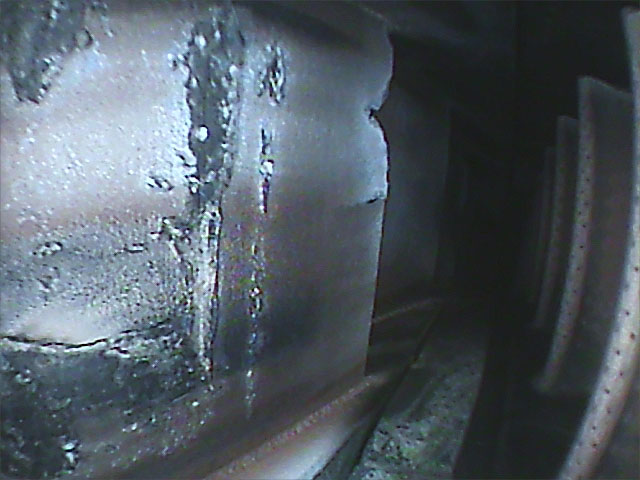
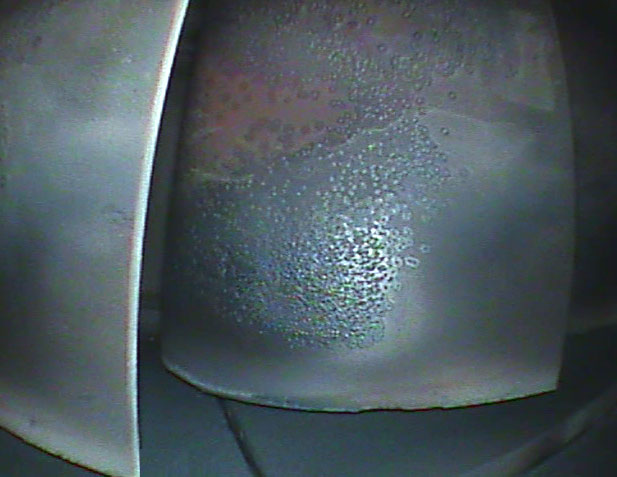
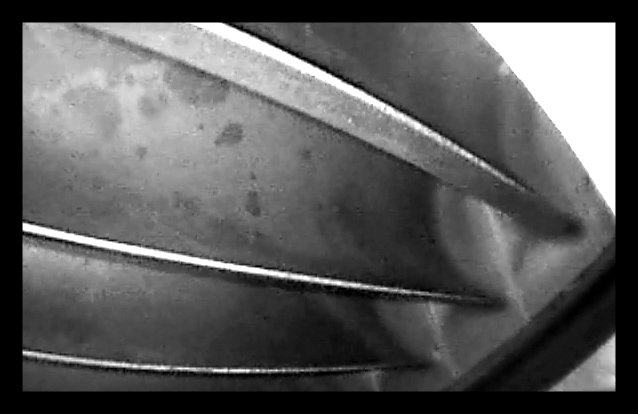
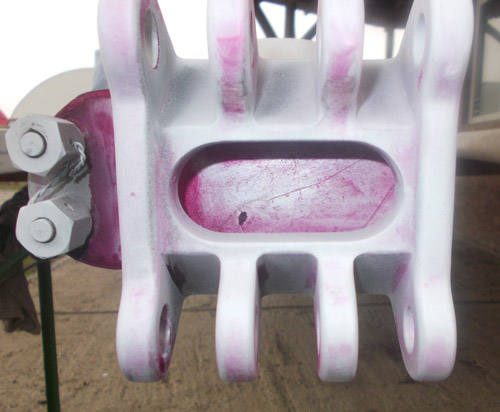
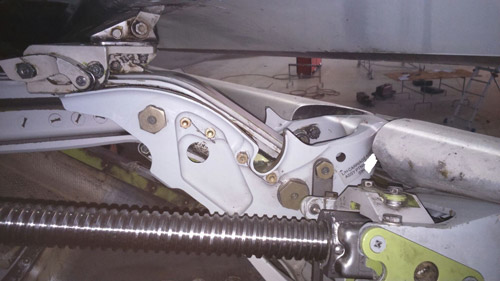
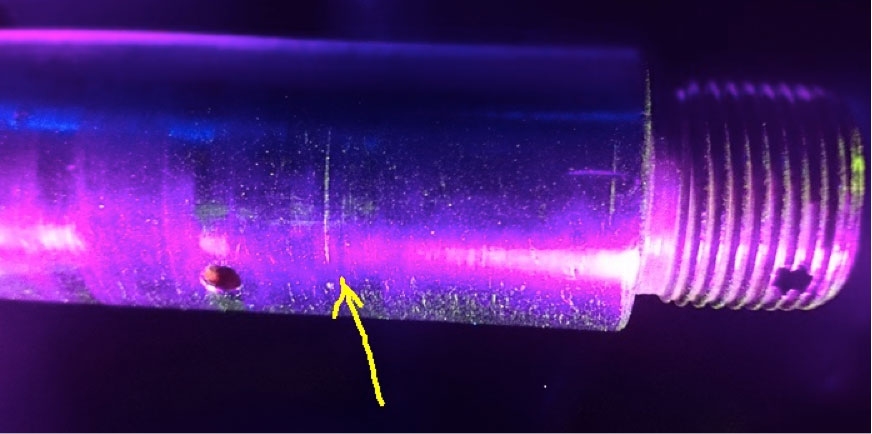
Considered as the right way for development, Sun Aviation has been initially authorized in 2012 by the Romanian CAA as a NDT Lab with capabilities to perform tests (Visual – Borescope, Ultrasound, Eddy Current Magnetic Particle and Liquid Penetrant) releasing the Test Report at the end. Where applicable, the reports are accompanied by annexes with pictures and video of the findings.
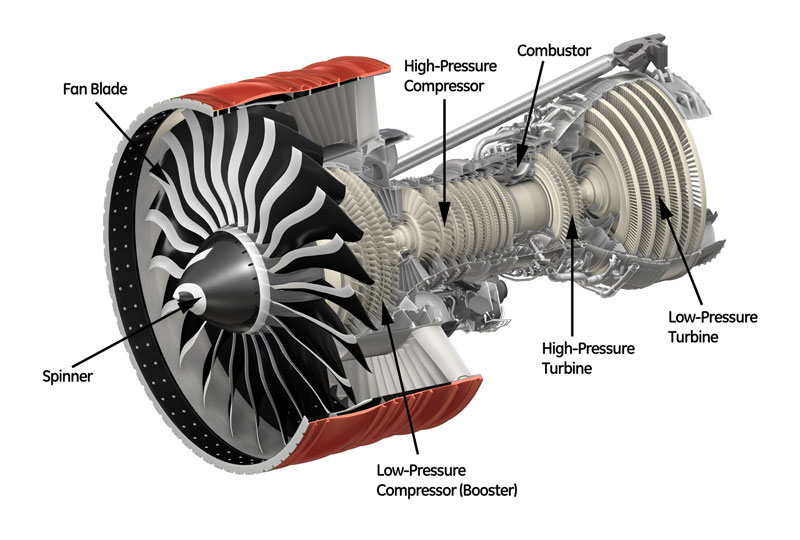
SUN AVIATION NDT Lab is capable to provide state-of-the-art standards inspections.
We provide inspections for civil and utility aircraft (both fix and rotary wing).
Now, the client portfolio contains major local operators with renewed contracts and regular tasks. There are, also, clients on order or clients with few tasks. Regardless the client status, our specialized engineers provide the highest level service.
For the methods that we are authorized, our Lab is fully prepared to provide services at the client location (local or abroad).
Lab’s activity is monitorized and managed trough our Q-Manager software, which integrates the quality and commercial side of the jobs. The software is own designed and tailored specifically for the NDT lab needs (starting from the aviation standards, EASA requirements and specific NDT rules).